基本情况
李秀珍(Dr. Xiuzhen LI),博士,博士生导师,主要从事东亚季风气候、区域水汽循环和极端降水等领域研究,特别是在南亚急流波列的传播及其气候影响、ENSO调控作用的新机制、水循环变异与降水异常等方向做了大量工作。近年来,在大气科学国内外具有较高影响力的学术期刊上发表SCI论文30多篇。获“广东省气象科技杰出青年奖”,曾主持中山大学“百人计划”项目、国家面上基金、青年基金和广东省面上基金等多个项目,参与国家重点研发项目2项。
联系方式
地址: 广东省珠海市唐家湾中山大学珠海校区海琴二号中山大学大气科学学院 邮编:519082
E-mail: lixiuzhen@mail.sysu.edu.cn
教育经历
2012.10–2012.12 瑞典哥德堡大学地球科学学院,访问博士生
2010.09–2013.08 香港城市大学能源与环境学院,博士
2008.09–2010.06 中山大学大气科学系,硕士
2004.09–2008 .06 中山大学大气科学系,学士
工作经历
2022.04–至今 中山大学大气科学学院,教授
2016.09–2022.04 中山大学大气科学学院,副教授
2015.09–2016.08 香港中文大学环境、能源及可持续发展研究所,博士后
2014.09–2015.08 香港中文大学地理与资源管理系,博士后
2013.09–2014.08 香港城市大学能源与环境学院,博士后
2010.01–2010.08 香港城市大学能源与环境学院,研究助理
学术兼职
担任国内外多个学术期刊的评审员:Clim. Dyn., Science Report, Atmos. Sci. Lett., Geophy. Res. Lett., Int. J. Climatol., Adv. Atmos. Sci., 热带地理, 等
讲授课程
《热带气象学》、《气象资料处理与可视化》、《现代热带气象学》
科研方向
-
东亚季风气候
-
南亚急流波列与冬季降水
-
厄尔尼诺-南方涛动(ENSO)与东亚水汽循环
-
全球变暖背景下极端天气/气候
科研项目
-
2022–2025国家自然科学基金面上项目:欧亚遥相关和南亚急流波列的耦合关系及其对东亚冬季降水的协同影响(主持);
-
2022–2024广东省自然科学基金面上项目:南亚急流波列对泛第三极地区积雪的影响及机制(主持)
-
2020–2023国家重点研发计划:大湾区高分辨率气象和大气化学成分再分析技术与数据集(参与)
-
2018–2021国家自然科学基金面上项目:南亚急流波列在冬季华南准静止锋维持中的作用 (主持);
-
2016–2021中山大学"百人计划二期"急需青年杰出人才项目(主持);
-
2016–2021国家重点研发计划:全球变暖背景下热带关键区海气相互作用及其对东亚夏季风气候的影响研究 (参与);
-
2015–2017国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目:我国东南、西南地区水汽收支的比较以及印缅槽的调控作用研究 (主持);
获奖与荣誉
-
广东省气象学会2019年度“广东省气象科技奖”
-
大气科学学院2020年度“我心中魅力教师”
-
香港城市大学 Research Tuition Scholarship (2011/2012, 2012/2013)
-
香港城市大学 Outstanding Academic Performance Award for Research Degree Students (2011-2012)
论著一览
一作或通讯:
- Zheng, M. L., and X. Z. Li*, Distinct patterns of monthly Southern Annular Mode events, Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aosl.2022.100206.
- Zhao, Y., Z. P. Wen, X. Z. Li*, R. D. Chen and G. X. Chen, 2021: Structure and maintenance mechanisms of the Mascarene High in austral winter, Int. J. Climatol., https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7498.
- 陈婉玲, 李秀珍*. 2021: 华南冬季强降水及高、低纬两支波列的协同影响, 大气科学, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2102.20246.
- Li, X. Z., W. R. Huang*. 2021: How long should the pre-existing climatic water balance be considered when capturing short-term wetness and dryness over China by using SPEI? Sci. of the Total Environ., 786, 147575.
- Li, X. Z.*. 2021: Maintenance of the South Asian jet wave train: Eddy kinetic energy balance, Clim. Dyn., https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05735-7.
- Huang, S. J., X. Z. Li*, Z. P. Wen, 2020: Characteristics and possible sources of the intraseasonal South Asian jet wave train in boreal winter, J. Climate, 33, 10523–10537.
- Li, X. Z.*, Z. P. Wen, W. R. Huang. 2020: Modulation of South Asian Jet wave train on the extreme winter precipitation over Southeast China: Comparison between 2015/16 and 2018/19, J. Climate, 33, 4065–4081.
- Li, X. Z.*, Z. P. Wen, D. L. Chen, Z. S. Chen. 2019: Decadal transition of interannual mode of moisture circulation over EA-WNP: bonding to different evolution of ENSO, J. Climate, 32, 289–308.
- Huang, S. J., X. Z. Li*, and Z. P. Wen. 2019: Interannual variation of the northern edge of summer monsoon in eastern China: Zonal discrepancies and impact factor, Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. DOI: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1812.18173 (in Chinese). 黄思洁,李秀珍*,温之平,2019: 东亚夏季风北界年际变化的东西差异及其影响因子[J]. 大气科学, 43(5): 1068-1080.
- Li, X. Z., X. Z. Tang, S. H. Li, M. Q. Mao, and Z. P. Wen*. 2018. Impact of the spring sensible heat flux over the Tibetan Plateau on summer rainfall over East China and its role in rainfall prediction. Acta Meteoro. Sinica, 76(6): 930–943 (in Chinese). 李秀珍,唐旭紫,李施华,简茂球,温之平*,2018: 春季青藏高原感热对中国东部夏季降水的影响和预测作用. 气象学报,76,930–943.
- Li, X. Z.*, N. C. Lau, and T. C. Lee, 2018: An observational study of the diurnal variation of precipitation over Hong Kong and the underlying processes, J. Appl. Meteor. Clim., 57, 1385–1402.
- Li, X. Z., Y. Q. D. Chen*, and W. Zhou, 2017: Response of winter moisture circulation to the India-Burma Trough and its modulation by the South Asian waveguide, J. Climate., 30, 1197–1210.
- Li, X. Z., and W. Zhou*, 2016: Modulation of the interannual variation of the India-Burma Trough on the Winter Moisture Supply over Southwest China. Clim. Dyn., DOI: 10.1007/s00382-015-2575-4.
- Li, X. Z., W. Zhou*, and Y. Q. D. Chen, 2015: Assessment of Regional Drought Trend and Risk over China: A Drought Climate Division Perspective. J. Climate, 28, 7025–7037.
- Li, X. Z., W. Zhou*, and Y. Q. D. Chen, 2015: Detecting moisture origin over Southeast China: Seasonal variation and heavy rainfall. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 33, 319–329.
- Li, X. Z., W. Zhou*, D. L. Chen, C. Y. Li, and J. Song, 2014: Water vapor transport and moisture budget over eastern China: Remote forcing from the two types of El Niño. J. Climate, 23, 8778–8792.
- Li, X. Z., W. Zhou*, C. Y. Li, and J. Song, 2013: Comparison of the annual cycles of moisture supply over Southwest and Southeast China. J. Climate. 26, 10139–10158.
- Li, X. Z., and W. Zhou*, 2012: Quasi-4-yr coupling between El Niño-Southern Oscillation and water vapor transport over East Asia-WNP. J. Climate, 25, 5879–5891.
- Li, X. Z., Z. P. Wen, W. Zhou*, and D. X. Wang, 2012: Atmospheric water vapor transport associated with two decadal rainfall shifts over East China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 90, 587–602.
- Li, X. Z., Z. P. Wen, and W. Zhou*, 2011: Long-term change in summer water vapor transport over South China in recent decades. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 89A, 271–282.
- Li, X. Z., W. Liang, Z. P. Wen, and R. S. Cai, 2011: Preliminary study on the salinity characteristics of South China Sea and its response to the summer monsoon. Journal of tropical oceanography, 30, 29–34 (in Chinese).
- Li, X. Z., W. Liang, and Z. P. Wen, 2010: Characteristics of the atmospheric water vapor and its relationship with rainfall in south China in northern autumn, winter and spring. J. Trop. Meteorol., 26, 626–632 (in Chinese).
其它:
- Li, J. C., Z. P. Wen, X. Z. Li, and Y. Y. Guo, 2021: Interdecadal changes in the relationship between wintertime surface air temperature over the Indo-China peninsula and ENSO. J. Climate, accept.
- Huang, W. R.*, P. Y. Liu, J. Hsu, X. Z. Li, and L. P. Deng. 2021a: Assessment of near-real-time satellite precipitation products from GSMaP in monitoring rainfall variations over Taiwan. Remote Sens., 13, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020202.
- Hsu, J., W. R. Huang*, P. Y. Liu, and X. Z. Li, 2021: Validation of CHIRPS precipitation estimates over Taiwan at multiple timescales. Remote Sens., 13, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020254.
- Zhu Y., Z. P. Wen*, Y. Y. Guo, R. D. Chen, X. Z. Li, and Y. T. Qiao, 2020: The characteristics and possible growth mechanisms of the quasi-biweekly Pacific–Japan teleconnection in boreal summer, Clim. Dyn., DOI:10.1007/s00382-020-05448-3
- Wang Z. W., Z. P. Wen, R. D. Chen, X. Z. Li, and S. H. Huang, 2020: Interdecadal enhancement in the interannual variability of the summer monsoon meridional circulation over the South China Sea around the early 1990s, Clim. Dyn., DOI: 10.1007/s00382-020-05375-3
- He Z. Q., W. Q. Wang, R. G. Wu, I. S. Kang, X. Z. Li, K. Xu and S. Chen, 2020: Change in coherence of summer rainfall variability over the western Pacific around the early 2000s: ENSO influence, J. Climate, DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0150.1.
- Guo, Y. Y., Z. P. Wen*, Y. K. Tan, and X. Z. Li, 2020: Plausible causes of the interdecadal change of the North Pacific teleconnection pattern in boreal spring around the late 1990s. Clim. Dyn., 55, 1427–1442, doi:10.1007/s00382-020-05334-y.
- Guo, Y. Y., Z. P. Wen, and X. Z. Li, 2020: Interdecadal change in the principal mode of winter–spring precipitation anomaly over tropical Pacific around the late 1990s. Clim. Dyn., 54, 1023–1042, doi:10.1007/s00382-019-05042-2.
- Zhang H. Y., Z. P. Wen*, R. G. Wu, X. Z. Li, R. D. Chen, 2019: An inter-decadal increase in summer sea level pressure over the Mongolian region around the early 1990s. Clim. Dyn., 52, 1935–1948, DOI: 10.1007/s00382-018-4228-x.
- Guo Y. Y., Z. P. Wen*, R. D. Chen, X. Z. Li, X. Q. Yang, 2020: Effect of boreal spring precipitation anomaly pattern change in the late 1990s over tropical Pacific on the atmospheric teleconnection. Clim. Dyn., 52, 401–416, DOI: 10.1007/s00382-018-4149-8.
- Huang S. H., Z. P. Wen*, Z. S. Chen, X. Z. Li, R. D. Chen and Y. Y. Guo, 2019: Interdecadal change in the relationship between the tropical easterly jet and tropical sea surface temperature anomalies in boreal summer, Clim. Dyn., 53, 2119–2131, DOI: 10.1007/s00382-019-04801-5.
- Zhu X. C., Y. Y. Guo, H. Y. Zhang, X. Z. Li, R. D. Chen, Z. P. Wen*, 2018: A southward withdrawal of the northern edge of the East Asian summer monsoon around the early 1990s. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 11(2), 136–142, DOI: 10.1080/16742834.2018.1410058.
- Qiu S., W. Zhou, Y. T. Leung, and X. Z. Li, 2017: Regional moisture budget associated with drought/flood events over China. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 4(36), DOI: 10.1186/s40645-017-0148-3.
- Wang, W. W., W. Zhou*, X. Z. Li, X. Wang, and D. X. Wang, 2016: Synoptic-scale characteristics and atmospheric controls of summer heat waves in China. Clim. Dyn., DOI: 10.1007/s00382-015-2741-8.
研究成果
1. ENSO对东亚水汽循环的调控作用及其年代际变化 (Li et al., 2019)
ENSO信号对东亚水汽循环的调控作用存在明显的年代际变化。El Niño消亡期夏季热带东太平洋海温冷、暖位相的转换快慢以及东印度洋海-气相互作用的强弱可导致东亚-西太水汽循环的主模态在1990年代初发生年代际转变。1990之后,El Niño(主要是东太平洋型El Niño)消亡期向La Niña转换较快,前期暖海温激发的大气环流异常在夏季迅速减弱,同期发展起来的东太平洋冷海温和东印度洋-海洋性大陆暖海温激发的西北太平洋反气旋位置明显偏南,强度减弱,范围扩大,导致夏季东亚-西太水汽环流模态发生相应的变化。环流北侧的降水异常由1990年之前位于长江中下游北移至1990年之后位于江淮流域。该研究进一步丰富了海温异常对东亚和西北太平洋夏季风的预测理论。
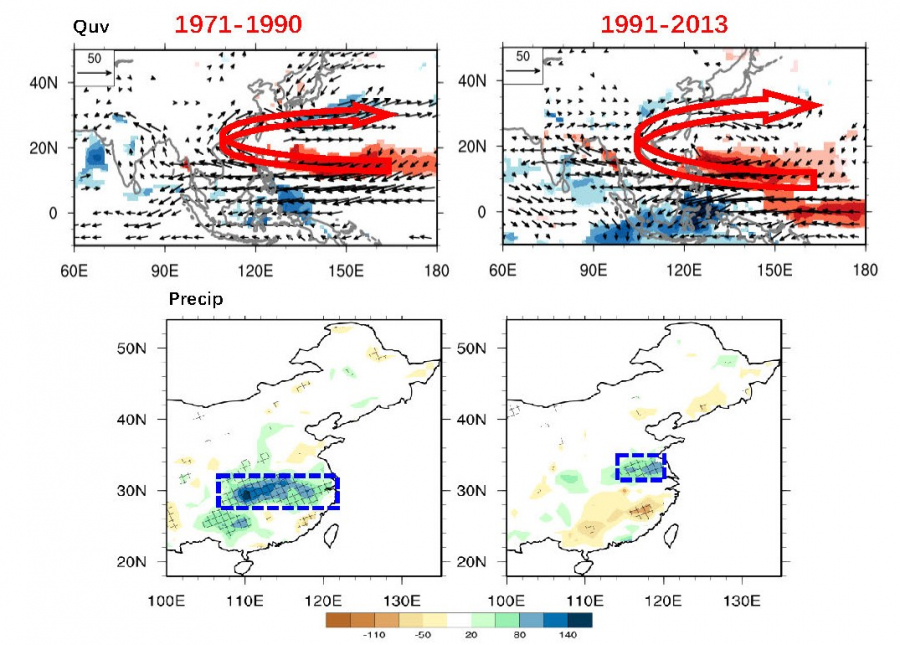
2. 冬季南亚急流波列对东亚水汽循环/降水的调控作用(Li et al., 2016; 2017)
南亚急流波列的传播可通过调控印缅槽的加深及东移影响中国南部水汽供应的事实。印缅槽的活动异常并不是局地的信号,而是扰动沿着南亚急流往下游传播的一部分,同时亦受到ENSO信号的调控。冬季印缅槽活动异常的信号来源可追溯至大西洋东岸,当扰动能量沿南亚急流波列传播至孟加拉湾时,印缅槽的迅速加深与El Niño在菲律宾激发的反气旋共同作用,增强了印缅槽槽前孟加拉湾、南海水汽往中国南部的输送。此波列信号是多尺度扰动综合的结果。天气尺度上,上游扰动可提前印缅槽异常6天出现。此发现有助于我们利用南亚急流波列传播优化我国南方冬半年降水的中、短期天气预报。进一步的工作还在进行当中。



