中山大学大气科学学院副教授,博士生导师,中山大学“百人计划”引进人才。中国科学院研究生院流体力学专业博士。目前主要研究方向为:山地-高原气候动力学、全球极端降水以及海气相互作用等。近期,在青藏高原上空联合发现、命名了一个大尺度大气环流型;提出全球小时降水强度存在“海-陆反向分布”现象。目前发表论文40余篇,H-index为18,国际学术会议特别邀请报告3次。担任Journal of Climate 杂志副编辑(Associate Editor),为Science Advances, Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, Communications Earth & Environment, Environmental Research Letters, Scientific Reports, Journal of Climate, Climate Dynamics, Geophysical Research Letters, Atmospheric Research等多个气候学杂志审稿人,是Elsevier出版社图书稿件审稿人。
"Research is what I'm doing when I don't know what I'm doing." — Wernher von Braun
“The secret of getting ahead is getting started. The secret of getting started is breaking your complex overwhelming tasks into small manageable tasks, and starting on the first one.” — Mark Twain
"Look up at the stars and not down at your feet." — Stephen Hawking
招生(长期有效)
欢迎有志于尝试科学研究工作的同学加入课题组,一起讨论趣味的科学问题、攀登壮美的科学高峰。鼓励本科生在毕业阶段,就尝试撰写、发表科技论文。招收硕士、博士研究生和博士后。欢迎有兴趣的同学联系。
联系方式
办公室地址: 广东省珠海市唐家湾中山大学珠海校区,大气科学学院,海琴2号楼A232室
邮编: 519082
邮箱地址: lixf87@mail.sysu.edu.cn
英文个人主页: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Xiao_Feng_Li3/research
受教育经历
博士:200509-200907,中国科学院大气物理研究所,地球流体力学专业
硕士:200209-200507,南京信息工程大学,气象学专业
学士:199809-200207,南京气象学院,天气动力学专业
工作经历
副教授,博士生导师:2020年8月至今,中山大学大气科学学院,主攻山地-高原气候动力学、全球极端降水和海气相互作用方向。
副研究员(Research Associate):2015年7月至2020年7月,英国纽卡斯尔大学(Newcastle University)工程学院(School of Engineering, previously named as “School of Civil Engineering and Geosciences”),主要从事青藏高原/山地天气气候动力学及全球极端降水的相关研究。
助理研究员:2009年1月至2015年6月,中国科学院大气物理研究所大气科学和地球流体力学数值模拟国家重点实验室,主要从事高纬度环状模动力学及热带海气相互作用方面的研究工作。
访问学者:2010年3月至2010年6月,美国阿拉斯加大学北极国际研究中心(IARC),从事环状模动力学方面的研究工作。
访问学者:2011年10月至2012年9月,澳大利亚联邦科学和工业研究组织(CSIRO)数学与信息科学研究所(CMIS),从事热带海气相互作用方面的研究工作。
研究兴趣
山地及青藏高原天气气候动力学
区域气候变化及全球变暖
极地气候及环状模动力学
全球水循环及极端降水
大气环流数值模拟及预测
热带海气相互作用
季风及气候热力学
主攻:山地-高原气候动力学、全球极端降水和海气相互作用方向。
课题承担情况
全球小时降水强度海-陆反向分布的形成和变化机理研究,国家自然科学基金面上基金,资助号42475036,项目主持人,2025.1-2028.12。
西青藏高原气旋的生成-维持机制及与周边大尺度环流系统相互作用研究,国家自然科学基金面上基金,资助号42175026,项目主持人,2022.1-2025.12。
西青藏高原大气环流对近地层大气辐射过程及地表气温影响机理研究,中国科学院大气所LASG开放课题,项目主持人,2022.1-2023.12。
西青藏高原大气再分析资料的适用性研究,高原大气环境四川省重点实验室开放课题,资助号PAEKL-2022-K08,项目主持人,2022.1-2023.12。
热带区域近海强风海气边界层物理过程及机理研究, 国家重点研发计划第四课题子课题,校级子课题主持人,资助号2023YFC3008002,2023.11.1-2026.10.31.
月内尺度北半球环状模对中国冬季环流异常的影响及机制,国家自然科学基金青年基金,资助号40905040,项目主持人 ,2010.1-2012.12。
亚洲区域海陆气耦合系统对南北半球大气质量交换的年际、年代际调制作用机理和模拟,亚洲区域海陆气相互作用机理及其在全球变化中的作用,国家重点基础研究计划(973),资助号2010CB950404,骨干及专题负责人,2010.6-2014.6。
月内尺度NAM的活动特征及其对北半球冬季环流异常的影响,中国科学院LASG自由探索项目, 项目主持人,2009.6-2011.6。
青藏高原和亚印太热力作用对亚洲季风年际、代际变化的影响,中科院知识创新工程重要方向项目,资助号KZCX2-YW-Q11-01,骨干及校级子课题主持人,2009.1-2011.12。
基于非均匀基本流的行星波传播新理论与亚澳季风相互作用,国家自然科学基金重点基金,资助号41030961, 项目成员,2011.1-2014.12。
南、北半球环状模对东亚季节性降水的影响机理及预测模型研究,公益性行业(气象)科研专项经费项目,资助号GYHY201306031,项目成员,2012.4-2015.12。
教授课程
《动力气象学》(本科)
《地球系统模式Linux/Unix基础与应用》(研究生)
研究生指导
在读
Yonglu Li (Supervision, Sep 2025-). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Taoyuan Shi (Supervision, Sep 2024-). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Jing Wang (Supervision, Sep 2023-). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Pengsheng Li (Supervision, Sep 2024-). Ph.D Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Jingzhi Wang (Supervision, Sep 2022-). Ph.D Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Chao Wang (Supervision, Sep 2021-). Ph.D Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
毕业
Binbo Lei (Supervision, Sep 2022-Aug 2025). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.("Outstanding Graduates of the 2025 at Sun Yat-sen University"/"2025届中山大学校级优秀毕业生")
Yangjie Jiang (Joint Supervision, Sep 2022- Aug 2024). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, China.
Pengsheng Li (Supervision, Sep 2021-Aug 2024). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Jingzhi Wang (Joint Supervision, Sep 2020-Aug. 2022). MS Program. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China.
Yafei Li (Joint Supervision, Sep. 2017-Aug. 2018). Exchanging Ph.D student from Beijing Normal University, China. School of Engineering, Newcastle University.
Qinqin Kong (Joint Supervision, Sep. 2016-Aug. 2017). Exchanging Ph.D student from CAS, China. School of Engineering, Newcastle University.
Muaz Zaim (Joint Supervision, Sep. 2016-Aug. 2017). Master's Degree. School of Engineering, Newcastle University.
学术兼职
Journal of Climate 杂志,副编辑(Associate Editor)。
广东省气象学会,第十三届理事会,气候与气候变化专业委员会,委员。
终生会员(Life Member,2011-),美国地球物理联合会(American Geophysical Union,AGU) 。
终生会员(Life Member,2015-), 欧洲地球科学联合会(European Geosciences Union,EGU)。
国际核心期刊审稿人(Expert Journal Reviewer),包括 Environmental Research Letters,Scientific Reports,Journal of Climate,Climate Dynamics,Geophysical Research Letters等。
爱思唯尔图书出版社图书稿件审稿人(Expert Book Proposal Reviewer of Elsevier)。
业务级软件和程序包提供: Software Packages Writing for USA National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA, in 2009) and China Meteorology Administration (CMA, in 2011) for their daily monitoring of the South American Summer Monsoon index and East Asia Summer Monson index. These software packages are still in use.
学术会议
国际邀请报告
Xiao-Feng Li, Yangjie Jiang, Xin Zhou, Song Yang, Impacts of the ENSO on the Western Tibetan Vortex. Section 9: Mountain Weather and Climate Change, International Mountain Forum 2024, 11-15 November 2024, Chengdu, China. (Invited oral)
Xiao-Feng Li, David Pritchard, Nathan Forsythe, Hayley J. Fowler, Increased Cycling of Moisture in Mountain Systems, GEO-GNOME Workshop “Essential Climate Variables for Observations in Mountains”,24-26 June 2019 UniS Building, Rooms A019, A024 and A027, University of Bern I Bern, Switzerland. (Invited oral)
Xiao-Feng Li, J. Yu, Y. Li and Hayley J. Fowler, Explaining recent wetting and cooling over Northern Australia: the importance of oceans under a warming climate, CliMathNet Conference 2016, 5th – 8th July, Newman Collaborative Lecture Theatre, Peter Chalk Centre, University of Exeter, United Kingdom (Invited oral, Plenary Speaker).
Xiao-Feng Li, Fluctuations of Northern Hemisphere Zonal-Mean Circulation: Phase Transition and Stratosphere-Troposphere Interactions, Pan-Pacific Climate/Weather Collaboration Meeting (PPCWCM), Sep. 8-10, 2009, Alaska, USA (Invited oral).
国内邀请报告
Xiao-Feng Li, The Western Tibetan Vortex as an emergent feature of near-surface temperature variation? 21 May 2021, Institute of Tibetan Plateau and Polar Meteorology, Chinese Academy of Meteorology Sciences, China (online oral).
Xiao-Feng Li, Climate extremes — A talk starts from hourly precipitation, 27 May 2021, Student Union of School of Atmospheric Sciences, Jiao Xue Lou D304, Sun Yat-Sen University (Zhuhai Campus), Zhuhai, China (Oral).
国际分会主持
Xiao-Feng Li, Co-Chair of Heat-waves, An International Commission on Dynamical Meteorology (ICDM) workshop 2012 on "Dynamics and predictability of high-impact weather and climate events", August 6-9, 2012, Kunming, China.
国际会议报告等
Xiao-Feng Li, Yangjie Jiang, Xin Zhou, Song Yang, Impacts of the ENSO on the Western Tibetan Vortex. A11S - Land-Atmosphere Interactions over the Tibetan Plateau and Their Impact on Weather and Climate, Including Extremes, AGU23 fall meeting, 12 December 2023, San Francisco, CA, USA. (Oral)
Xiao-Feng Li, Hayley J. Fowler, Nathan Forsythe, Jingzhi Wang, Song Yang, The Western Tibetan Vortex and its Impacts on Air Temperature. Section 2: Climate/weather impact and adaptation, TEWEX-CLIMA 2023, 10 August 2023, Shangri-La, Yunnan, China. (Oral)
Xiao-Feng Li, Jingjing Yu, The Western Tibetan Vortex as an emergent feature of near-surface temperature variation? EGU2020-19376, Online | 4–8 May 2020, the EGU General Assembly 2020 online (Oral)
Xiao-Feng Li, J. Li, and X. Zhang, Fluctuations of Northern Hemisphere Zonal-Mean Circulation: Phase Transition and Stratosphere-Troposphere Interactions, J-M04: Stratosphere-Troposphere-Ocean coupling in weather and climate, IUGG 2011, XXV General Assembly, June 28-July 7, 2011, Melbourne, Australia (Oral).
Xiao-Feng Li, Hayley Fowler, Nathan Forsythe, Jingjing Yu, David Pritchard, and Stephen Blenkinsop. A Newly Recognized Large-scale Circulation System Governing the Western Tibetan Climate — the Western Tibetan Vortex. CL4.30/AS4.47/CR1.13/HS11.22 - Mountain climatology and meteorology, Tuesday, 09 Apr 2019, European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2019, Vienna, Austria (Poster)
Xiao-Feng Li, Hayley Fowler, and Stephen Blenkinsop, Impacts of the North Atlantic Oscillation on Frequencies of Daily Precipitation Extremes over the UK in winter, EGU2017-10704, CL5.05, 23–28 April 2017, European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2017, Vienna, Austria (Posters).
Xiao-Feng Li, Jianping Li, Yun Li, Jingjing Yu, Hayley Fowler, Stephen Blenkinsop, et al., Role of Global Warming in recent Speedup of the Wintertime Pacific Walker Circulation, EGU2017-6926, CL4.17/AS1.16/OS1.22, 23–28 April 2017, European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2017, Vienna, Austria (Posters).
主要论文列表
Submitted
Taoyuan Shi, Xiao-Feng Li*, Kaiqiang Deng, Song Yang. 2026: Warming Tropical Western Pacific Fuels More Frequent Winter Surface Wind Extremes over the South China Sea. Submitted
Jing Wang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Song Yang, Xin Lai. 2025: Elevation and Cloud Dependent Seasonal Cycles of Surface Air Temperature over the Tibetan Plateau. Submitted
Xiao-Feng Li, Jianping Li, Yun Li, Song Yang, Cheng Sun, Jingjing Yu, Hayley J. Fowler, Stephen Blenkinsop, Ruiqiang Ding, Sen Zhao, Lei Wang, Fei Zheng, Yanjie Li, Juan Feng, Taoyuan Shi. 2025:Contrasting SST Modes Explain Decadal Intensification of Pacific Walker Circulation. Submitted (under the first round of review)
2026
Jingzhi Wang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Jing Wang, Song Yang, Hayley J. Fowler. 2026: Radiative forcing of Western Tibetan Vortex on surface air temperature in spring. Geophysical Research Letters. 53(3), e2025GL119603, DOI: 10.1029/2025GL119603. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.66,PDF)
- Yangjie Jiang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Xin Zhou, Song Yang, Hayley J. Fowler. 2026: Amplification of ENSO's Influence on the Atmospheric Circulation over Western Tibetan Plateau during 1948-2021. Global and Planetary Change. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2026.105397. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.0,PDF)
2025
Jing Wang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Jingzhi Wang, Xin Lai, Song Yang, Nathan Forsythe, Hayley J. Fowler. 2025:Evaluation of Reanalyzed Surface Air Temperature over the Western Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Research. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2025.108454. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.4, PDF)
Jingzhi Wang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Song Yang, Nathan Forsythe, Hayley J. Fowler. 2025:Impact of the Western Tibetan Vortex on Springtime Snow Cover over the Western Tibetan Plateau. Geophysical Research Letters.52(14):e2024GL114453. DOI: 10.1029/2024GL114453. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.66,PDF)
Binbo Lei, Xiao-Feng Li*, Yanjie Li and Song Yang. 2025: Impacts of NAO on Western Tibetan Vortex: Summer Versus Winter Features. Journal of Tropical Meteorology. DOI:10.3724/j.1006-8775.2025.037. (SCI, Impact Factor=1.06,PDF)
Binbo Lei, Xiao-Feng Li*, Yanjie Li, Song Yang, Hayley J. Fowler, Nathan Forsythe. 2025: A synoptic view of the Western Tibetan Vortex. Atmospheric Research. 325(15): 108232. DOI : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2025.108232. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.4, PDF)
Yangjie Jiang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Xin Zhou, Song Yang, Hayley J. Fowler, Binbo Lei. 2025: Impacts of ENSO on Atmospheric Circulation over the Western Tibetan Plateau in Autumn. Journal of Climate. 38(16): 4251–4261. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-24-0443.1. (SCI, Impact Factor=5.38, PDF)
Pengsheng Li, Xiao-Feng Li*, Jingjing Yu, and Song Yang. 2025: Land-Sea Contrast of Global Hourly Precipitation Intensity in ERA5: Dominant Role of Convective Precipitation. Geophysical Research Letters, 52(10): e2025GL114733. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1029/2025GL114733. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.66,PDF)
2024
- Taoyuan Shi, Wanlei Liu, Xiao-Feng Li, Tuantuan Zhang, Shaobo Qiao, Wei Yu, Lianlian Xu, Kaiqiang Deng. 2024: Comparative Analysis of the 2013 and 2022 Record-Breaking Heatwaves over the Yangtze River Basin. Ocean-Land-Atmos Res, 3:0071. DOI:10.34133/olar.0071. (PDF)
- Wang, R., F. Zheng, and X. Li, 2024: Influence of the Southern Ocean Dipole on the inter-model diversity of temporal trend of the austral summer Southern Annular Mode in CMIP6 models. Climate Dyn., 62, 7019-7036. Doi:10.1007/s00382-024-07263-6. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.563, PDF)
- LI Pengsheng, LI Xiaofeng*, YANG Song,2024. Evaluation of the global hourly precipitation frequency in ERA5 using multiple satellite datasets[J]. Trans Atmos Sci,47(2):249-259. DOI:10.13878/j. cnki. dqkxxb.20240302018.(CSCD, PDF)
- Yangjie Jiang, Xin Zhou, Quanliang Chen, Wuhu Feng, Xiao-Feng Li, and Yang Li; 2024: Secular changes in the tropical stratospheric water vapour entry induced by the Indo-Pacific warm pool warming. Atmospheric Research, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2024.107381. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.4,PDF)
2022
Jingzhi Wang, Xiao-Feng Li*, Shaofeng Liu, Ting Liu, Yongjiu Dai, Song Yang, Hayley Fowler. 2023: Leading Modes of Wind Field Variability over the Western Tibet Plateau. Climate Dynamics. DOI : 10.1007/s00382-022-06358-2. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.563, PDF)
2021
Xiao-Feng Li*, Jingjing Yu, Shaofeng Liu, Jingzhi Wang, Lei Wang, 2022: Structure of the Western Tibetan Vortex Inconsistent with a Thermally-Direct Circulation. Climate Dynamics. DOI : 10.1007/s00382-021-06001-6. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.563, PDF)
Fowler, H. J., H. Ali, R. P. Allan, N. Ban, R. Barbero, P. Berg, S. Blenkinsop, N. S. Cabi, S. Chan, M. Dale, R. J. H. Dunn, M. Ekström, J. P. Evans, G. Fosser, B. Golding, S. B. Guerreiro, G. C. Hegerl, A. Kahraman, E. J. Kendon, G. Lenderink, E. Lewis, X. Li, P. A. O'Gorman, H. G. Orr, K. L. Peat, A. F. Prein, D. Pritchard, C. Schär, A. Sharma, P. A. Stott, R. Villalobos-Herrera, G. Villarini, C. Wasko, M. F. Wehner, S. Westra, and A. Whitford, 2021: Towards advancing scientific knowledge of climate change impacts on short-duration rainfall extremes. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 379. Doi:10.1098/rsta.2019.0542. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.275,PDF)
Thornton, J. M., E. Palazzi, N. C. Pepin, P. Cristofanelli, R. Essery, S. Kotlarski, G. Giuliani, Y. Guigoz, A. Kulonen, D. Pritchard, X. Li, H. J. Fowler, C. F. Randin, M. Shahgedanova, M. Steinbacher, M. Zebisch, and C. Adler, 2021: Toward a definition of Essential Mountain Climate Variables. One Earth. Doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2021.05.005. (SCI, Impact Factor=14.944, PDF)
2020
Li, X.-F., S. Blenkinsop, R. Barbero, J. Yu, E. Lewis, G. Lenderink, S. Guerreiro, S. Chan, Y. Li, H. Ali, R. Villalobos Herrera, E. Kendon, and H. J. Fowler, 2020: Global distribution of the intensity and frequency of hourly precipitation and their responses to ENSO. Climate Dynamics, 54, pages4823–4839. Doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05258-7.(SCI, Impact Factor=4.563, PDF)
Yu J, Li X-F, Lewis E, Blenkinsop S, and Fowler HJ, 2020: UKGrsHP: a UK high-resolution gauge–radar–satellite merged hourly precipitation analysis dataset. Climate Dynamics. Doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05144-2. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.563, PDF)
Kong Q, Guerreiro SB, Blenkinsop S, Li X-F, and Fowler HJ, 2020: Increases in summertime concurrent drought and heatwave in Eastern China. Weather and Climate Extremes, 28, 10024 (SCI, Impact Factor=4.698, PDF)
Yafei Li, Daniel Argueso, Stephen Blenkinsop, Jason Evans, Geert Lenderink, Xiaodong Yan, Selma Guerreiro, Elizabeth Lewis, Xiao-Feng Li. 2019: Strong intensification of hourly rainfall extremes by urbanization. Geophysical Research Letters. Doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL088758. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.339, PDF)
2019
Li, X-F, H. J. Fowler, J. Yu, N. Forsythe, S. Blenkinsop. 2019: Thermodynamic Controls of the Western Tibetan Vortex on Tibetan Air Temperature. Climate Dynamics. 53(7):4267-4290. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-019-04785-2. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.563, PDF)
Champion, A.J., Blenkinsop, S., Li, X-F, Fowler, H.J. 2019: Synoptic-scale precursors of extreme UK summer 3-hourly rainfall. Journal of Geophysical Research. DOI: 10.1029/2018JD029664. (SCI, Impact Factor=3.38, PDF)
Lewis, E., Fowler, H.J., Alexander, L., Dunn, R., McClean, F., Barbero, R., Guerreiro, S., Li, X-.F., Blenkinsop, S. GSDR: A global sub-daily rainfall dataset. Journal of Climate. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0143.1. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.661, PDF)
Ding, R., Li, J., Tseng, Y-H., Sun, C., Nan, L., Xing, Li, X-F, 2019: Linking the North American dipole to the Pacific meridional mode. Journal of Geophysical Research. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029692. (SCI, Impact Factor=3.38, PDF)
Barbero, R., H. J. Fowler, S. Blenkinsop, S. Westra, V. Moron, E. Lewis, S. Chan, G. Lenderink, E. Kendon, S. Guerreiro, X.-F. Li, R. Villalobos, H. Ali, and V. Mishra, 2019: A synthesis of hourly and daily precipitation extremes in different climatic regions. Weather and Climate Extremes, 26, 100219. (Impact Factor=4.698, PDF)
Pritchard DMW, Forsythe N, Fowler HJ, O’Donnell GM, and Li X-F, 2019: Evaluation of Upper Indus near-surface climate representation by WRF in the High Asia Refined Analysis. Journal of Hydrometeorology. 10.1175/JHM-D-18-0030.1. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.661, PDF)
2018
Li, X-F, H. J. Fowler, N. Forsythe, S. Blenkinsop. 2018: The Karakoram Vortex over the Western Tibetan Plateau: Seasonal and Inter-Annual variability. Climate Dynamics. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-018-4118-2. (SCI, Impact Factor = 4.563, PDF)
Blenkinsop S, Fowler HJ, Barbero R, Chan SC, Guerreiro SB, Kendon E, Lenderink G, Lewis E, Li X-F, Westra S, Alexander L, Allan RP, Berg P, Dunn RJH, Ekström M, Evans J, Holland G, Jones R, Kjellström E, Klein-Tank A, Lettenmaier D, Mishra V, Prein AF, Sheffield J, Tye MR. 2018: The INTENSE project: using observations and models to understand the past, present and future of sub-daily rainfall extremes. Advances in Science & Research, 15, 117–126. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/asr-15-117-2018. (SCI, Impact Factor = 1.529, PDF)
Guerreiro SB, Fowler HJ, Barbero R, Westra S, Lenderink G, Blenkinsop S, Lewis E, and Li, X-F,2018: Detection of continental-scale intensification of hourly rainfall extremes. Nature Climate Change, 8, 803-807. DOI: 10.1038/s41558-018-0245-3. (SCI, Impact Factor=22.363, PDF)
2017
N. Forsythe, H. J. Fowler, Xiao-Feng Li, S. Blenkinsop and D. Pritchard. 2017: Karakoram temperature and glacial melt driven by regional atmospheric circulation variability. Nature Climate Change, 7, 664–670. DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE3361. (SCI, Impact Factor=22.363, Personal significant contributions are in identifying the Karakoram Vortex and its physical mechanisms, PDF)
2015
Xiao-Feng Li, J. Li, Y. Li. 2015: Recent Winter Precipitation Increase in middle-lower Yangtze River Valley since the late 1970s: A response to warming in tropical Indian Ocean. J. Climate, 28(9), 3857–3879. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00701.1.( SCI, Impact Factor=4.661, PDF)
Zheng, F., J. Li, L. Wang, F. Xie, and Xiao-Feng Li, 2015: Cross-Seasonal Influence of the December–February Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode on March–May Meridional Circulation and Precipitation. J. Climate, 28(17), 6859-6881. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.661, PDF)
Xiao-Feng Li. 2015:Review on the Introduce and Debates of the Annular Modes. Advances in Earth Science (In Chinese). 30(3), 367-384.(CSCD, PDF)
2014
Xiao-Feng Li, J. Li, X. Zhang and C. Sun, 2014: Role of Ferrel cell in daily variability of Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode, Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(27), 3457-3464. CSB-2013-1144.R6. (SCI, Impact Factor= 4.092, PDF)
Yu, J., Y. Liu and Xiao-Feng Li, 2014: Connections between the Dominant Modes of Westerly over the Upstream Region of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and the Regional Precipitation of China and NAO in Winter, Plateau Meteorology (In Chinese), 33(4), 877-886.( CSCD, PDF)
2013
Xiao-Feng Li, J. Yu, and Y. Li, 2013: Recent Northern Australia summer rainfall increasing and surface cooling since the late 1970s: A Response to Warming in the Tropical Western Pacific, J. Climate, 26(18), 7221–7239, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00786.1. (SCI, Impact Factor=4.661, PDF)
Xiao-Feng Li, J. Li, and X. Zhang, 2013: A Two-way Stratosphere–Troposphere Coupling of Submonthly Zonal-Mean Circulations in the Arctic, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 30(6), 1771-1785. doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2210-4. (SCI, Impact Factor= 1.338, PDF)
2012 and Before
Xiao-Feng Li, and J. Li, 2012: Analysis of the Quasi-geostrophic Adjustment Process of the Southern Hemisphere Annular Mode. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. (In Chinese), 36(4), 755-768. (CSCD, PDF)
Xiao-Feng Li, and J. Li, 2011: Meridional and vertical propagation characteristics of submonthly Northern Hemisphere Annual Mode. Acta Meteor. Sin. (In Chinese), 69(6), 1046-1061. (CSCD, PDF)
Xiao-Feng Li, and J. Li, 2010: Propagation characteristics circulation anomalies of sub-monthly Southern Hemisphere annular mode. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. (In Chinese), 34(6), 1099-1113. (CSCD, PDF)
Xiao-Feng Li, and J. Li, 2009: Main submonthly timescales of Northern and Southern Hemisphere annual modes. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. (In Chinese), 33(2), 215-231. (CSCD, PDF)
Xiao-Feng Li, P. Guo, L. Dong. Onset Process of Summer Somali Jet and Possible Influenced Mechanism. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology (In Chinese), 2006, 29(5): 599-605. (CSCD, PDF)
L. Dong, P. Guo, Xiao-Feng Li. Relationship between Activity of Transient Waves and Excessive/Deficit Summer Rain in Changjiang-Huaihe River Basin, Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology (In Chinese), 2006, 29(4): 470-476. (CSCD, PDF)
气候分析常用(子)程序下载 // NCL SCRIPTS and SUBROUTINES FOR CLIMATE ANALYSIS
Please download those functions and procedures by directly clicking their names. Examples of how to using them are also provided behind. If you have any questions please contact me through lixf87@mail.sysu.edu.cn, thanks. (Updated on 3rd March 2023)
请直接点击程序名下载。如有任何问题请联系我: lixf87@mail.sysu.edu.cn, 谢谢!(更新于2023年3月3日)
在地图背景上绘制长江黄河。// This sub-procedure creates and attaches polylines of Yangtze River and Changjiang River to a given plot. See an example and its output figure. This script and example are also provided to the NCL website. |
输出数据为short型的Netcdf格式文件。Short型NC文件只需要float型NC文件一半的磁盘容量。// This sub-procedure outputs short Format Netcdf file by using an EFFICIENT way, which saves a half disk volume. See an example. |
万能读入子程序,内核为addfile函数,读单个数据文件。可读出数据文件(inf)指定变量(var)在指定维数 (通过opt给定参数:opt@t, opt@x, opt@y, opt@z)上的数值。若不通过opt给定参数,则读出该变量全维度数值。注意:readVar2需要调用另外另个子程序indTime and numNum,已在后面的调用范例中给出。// This is a wrapped function of the "addfile", which is used to read a variable (defined by "var") from a data file (defined by "inf") on given dimensions through assigning meta data (opt=True, and opt@t=(/t1,t2/), opt@x=(/x1,x2/), opt@y=(/y1,y2/), opt@z=(/z1,z2/)) or the whole dimension of the variable will be read out (opt=False). See an example. As "readVar2" will call indTime and numNum, so please load functions of "indTime" and "numNum" before using readVar2 as did in the example. |
分年绘制时间序列类指数图,并指示所挑选事件。// This script shows how to create a series of XY plots attached along the X and Y axes, with specific areas filled for emphasis.This script plots daily index highlighted with polygons year by year. This is a typical plot that people see in papers of climate studies. The plots are paneled using gsn_panel. Because they are different sizes, it was necessary to set gsnPanelScalePlotIndex to 1 (the top middle plot), indicating that this plot should be used to determine the scale factor for resizing all the plots. Otherwise, you will be unable to see the X axis labels on the bottom three plots. Also see unique11.ncl in NCL official website. |
友情链接 // Links to other Websites
Academic Journals
Science Science Advances
Nature Nature Climate Change Nature Geosciences
- npj Climate and Atmospheric Science Nature Communications
Scientific Data Earth System Science Data
Science Bulletin National Science Review
Climate Dynamics Journal of Climate
Earths Future Current Climate Change Reports
ERL GRL JGR
Weather and Climate Extremes
期刊影响影子查询 中科院期刊杂志分区查询
Purchased Softwares for Windows Operating System by SYSU
Free softwares and Commands
- NCL GrADS NCO Python Fortran Netcdf
- SSH Clients for Windows (Putty, FileZilla etc)
- SFTP LFTP SCP RCP GREP FIND MAKE
- MPI Open-MPI
- Linux/Unix Putty FileZilla
Fortran Compliers and Subroutines
Numerical Models
Reanalysis datasets
- Gridded climate datasets from NOAA, including NECEP1/2, ERSST, CPC Precipitation etc.
- Reanalysis datasets from ECWF, including ERA40, ERA_Interim, ERA5, ERA-20C and etc.
- Reanalysis datasets from NASA, including MERRA, MERRA-2 and GMAO Reanalysis Products.
- Reanalysis datasets from JRA, including JRA-55, JRA-25 and DSJRA-55.
趣味科研 // Do you know these interesting facts?
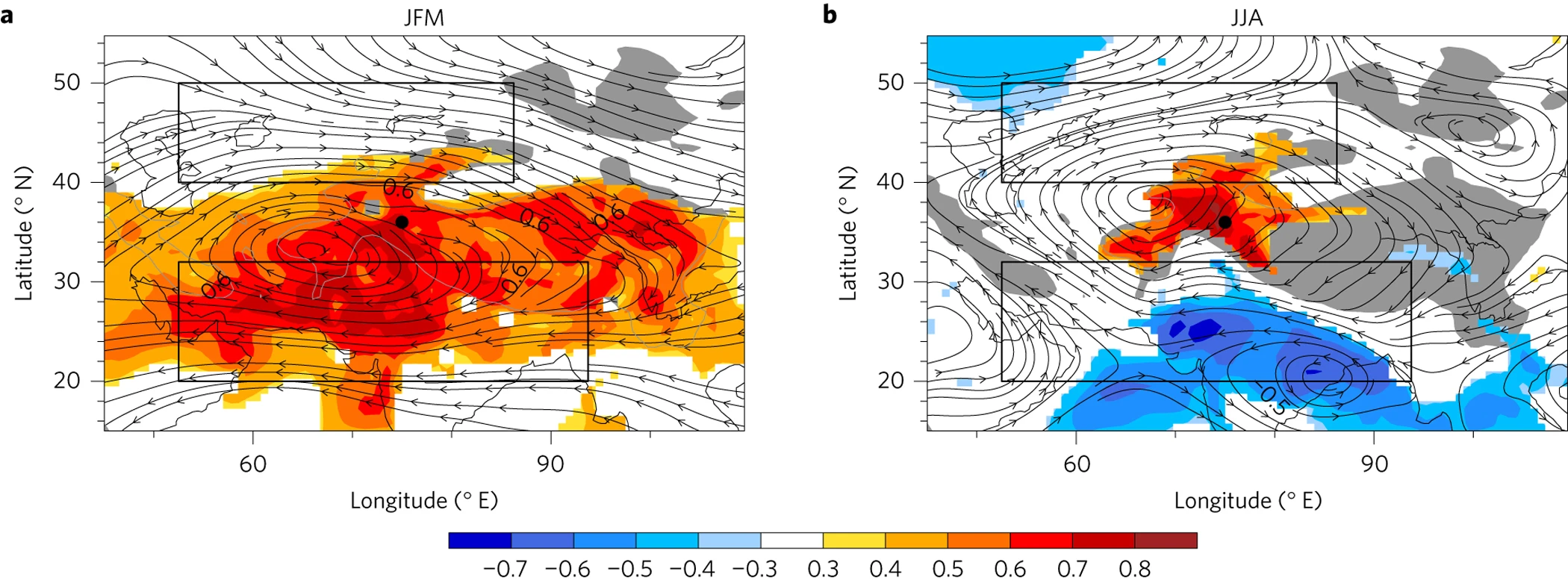
你知道西青藏高原上空存在一个大尺度大气环流型 Western Tibetan Vortex (WTV)么?这是一个对西青藏高原具有重要影响的、四季均存在的、具有深厚结构的、东西半径可达印度半岛3~4倍的大尺度大气环流型 (Forsythe et al, 2017; Li et al, 2018)。// Do you know the Western Tibetan Vortex (WTV)?It is a large scale atmospheric pattern with deep structure centering at the western Tibet Plateau. The annual mean WTV extends from ~ 50° E to ~ 105° E (equivalent to ~ 5500 km), spanning 3–4 times the west–east breadth of the Indian Peninsula. The WTV is the dominant driver of tropospheric atmospheric variability over the western Tibetan Plateau in most seasons, with a wider regional influence on near-surface climate. The WTV, also called as the Karakoram Vortex (KV), is recognized by the first two publications from the same research team, i.e. Forsythe et al. (2017) and Li et al. (2018) (those two are usually cited together in recent publications), except that the former one is focus more on its impacts on glaciers but the later one is more focus on the basic features of the KV/WTV itself. For more details please read Forsythe et al. (2017) and Li et al. (2018).
你知道山地气候观测中,科学家们目前最关心的变量是哪些么?图中单词的尺寸越大,代表科学家们越关心这个变量,比如 albedo,precipitation,air temperature,water moisture 和 land cover。这些变量可能成为未来世界山地气候观测中的侧重点。而如何将这些变量在山区观测地更准确,则需要科学家和科技工作者们将来更多的努力。// Do you know what variables interested the mountain climate scientists most?The bigger size of the word in the below figure, more important the variable is according to mountain climate scientists nowadays. For example, albedo, precipitation, air temperature, water moisture, land cover and etc. These could be the the focus in the mountain observations in the future. How to observe them more accurate in mountain ares needs more efforts in the near future. For more details please read Thornton et al. (2021).


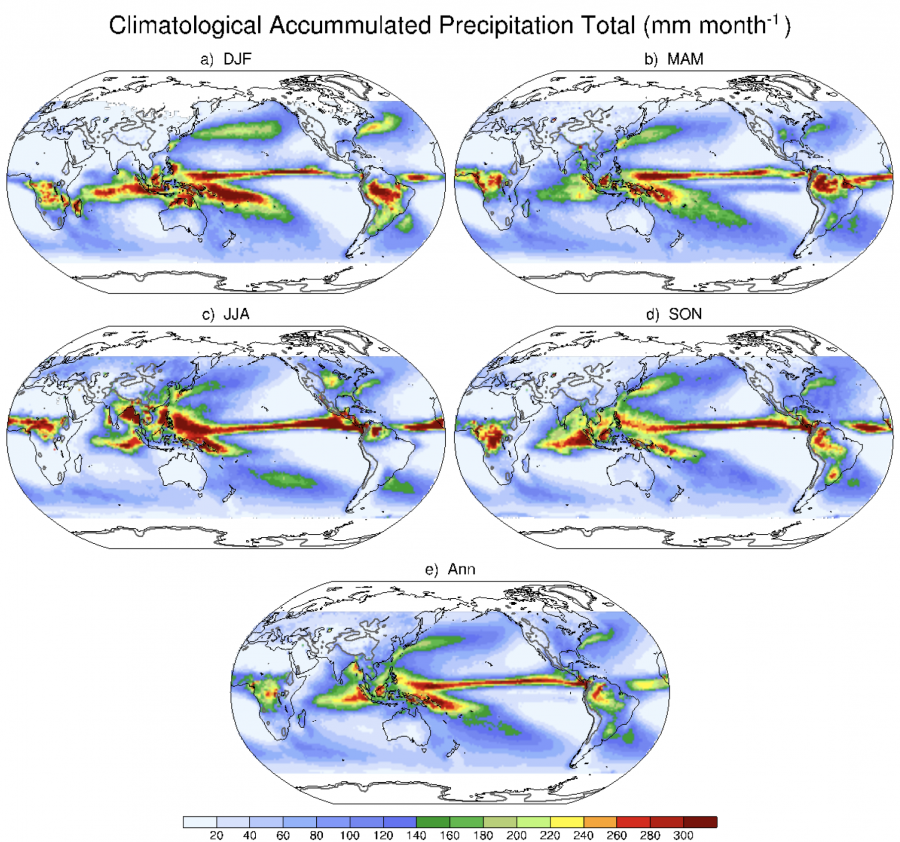
你知道全球小时降水具有独特的(不同于逐日及更长时间尺度降水)分布特征么?小时降水强度 (平均和极端) 大值中心主要分布在陆地上,而非水汽充足的海上。这种小时降水独特的分布特征,在以前的研究中很少被注意到。而日降水等低频降水的强度(平均和极端)中心主要是分布在海上的,这符合海上水汽供应足、降水自然多的预期。下图给出了降水强度分布特征从逐小时、到3小时、再到逐日尺度的明显转变。可见,小时降水与逐日等低频时间尺度降水非常不同,值得深入研究。两个值得思考的问题是:(1) 为何小时降水最强中心在陆地而非海洋?(2) 降水的间歇性在小时尺度上是否比日尺度上被表达的更加准确呢?// Do you know that the hourly mean (or extreme) intensity of precipitation has its unique distributions features? The highest mean (or extreme, for example the 99% percentile) hourly precipitation intensity (HPI) values are mainly located over continental areas (where is poor of moisture) rather than over oceanic areas (where is rich of moisture). This unique distribution feature is not evident in daily or coarser resolution data, which has seldom been noticed by previous studies.Two relevant interesting questions could be:(1) why the highest hourly precipitations are mainly located at the land areas instead of oceanic areas? (2) how well does the intermittence features of precipitation represented in the hourly timescale than in other timescales?These need our deeper thinking. For more details please read Li et al. (2020).

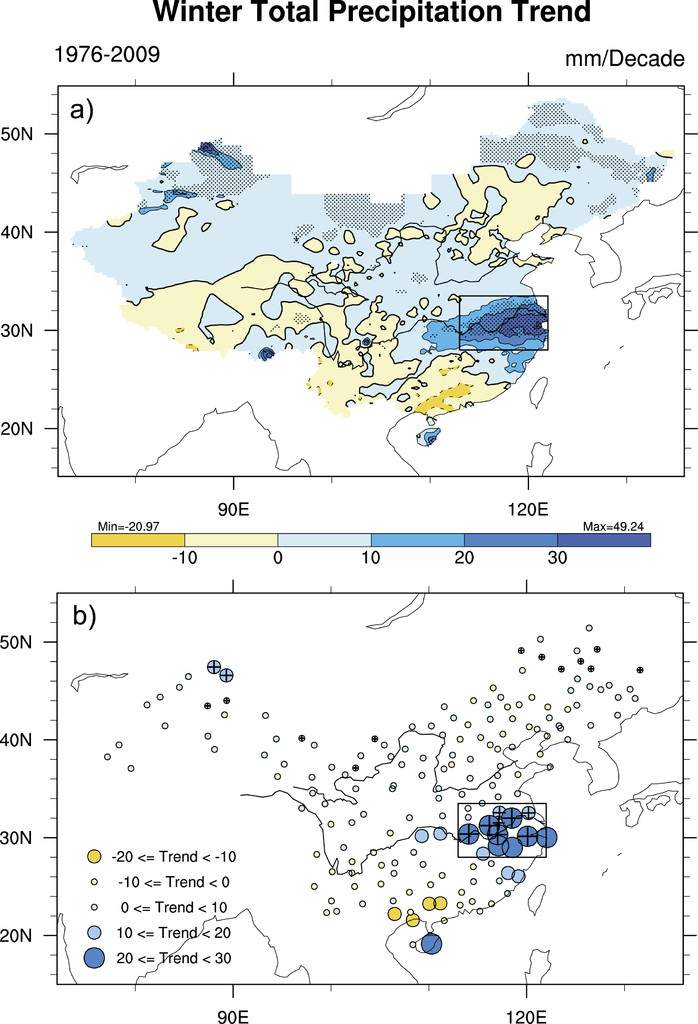
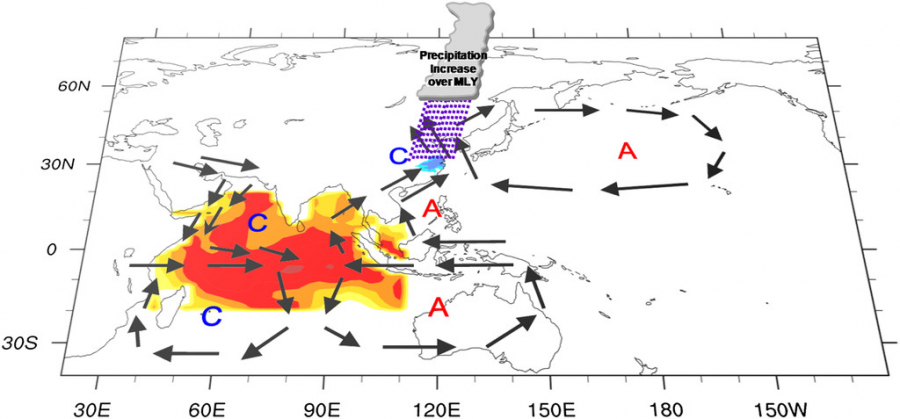
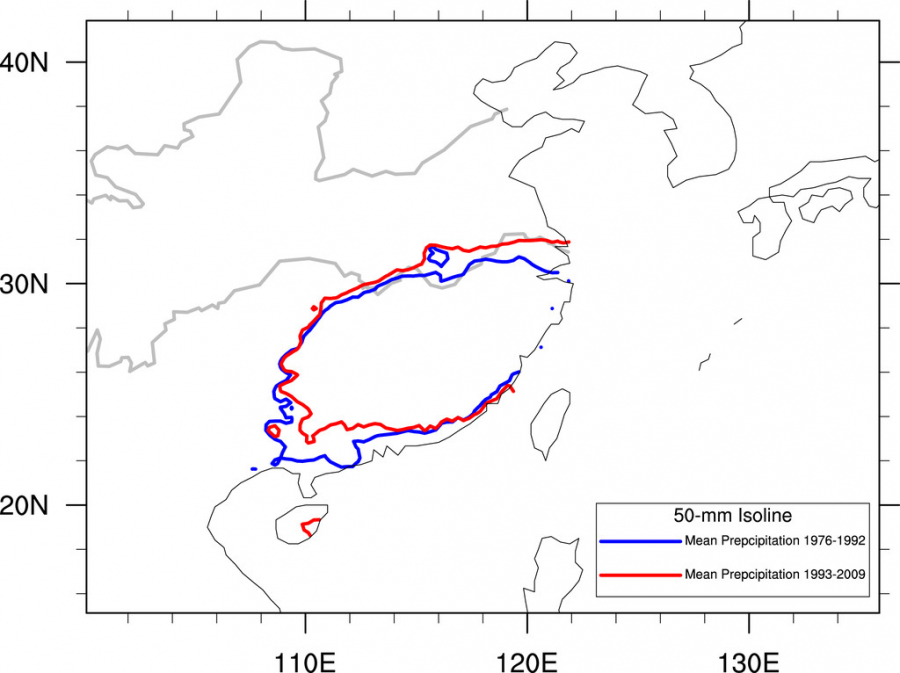
你知道长江中下游冬季雨雪过去几十年为何会增多么?印度洋增暖是主要原因,贡献超过80%。冬季印度洋增暖引起华南雨带北推,造成长江中下游冬季雨雪增多(换而言之:长江中下游降水异常增多,对应的实际上是气候态降水的向北移动和扩展)。// Do you know why the middle-lower Yangtze River Valley (MLY) was wetting in winter during the three decades since the late 1970s?Actually, 80% of the observed wetting trend over the MLY is due to the tropical Indian Ocean (TIO) warming. TIO warming causes the northward extension of the climatological mean precipitation belt over southern China, resulting in the MLY wetting in winter since 1970s. For more details please read Li et al. (2015).
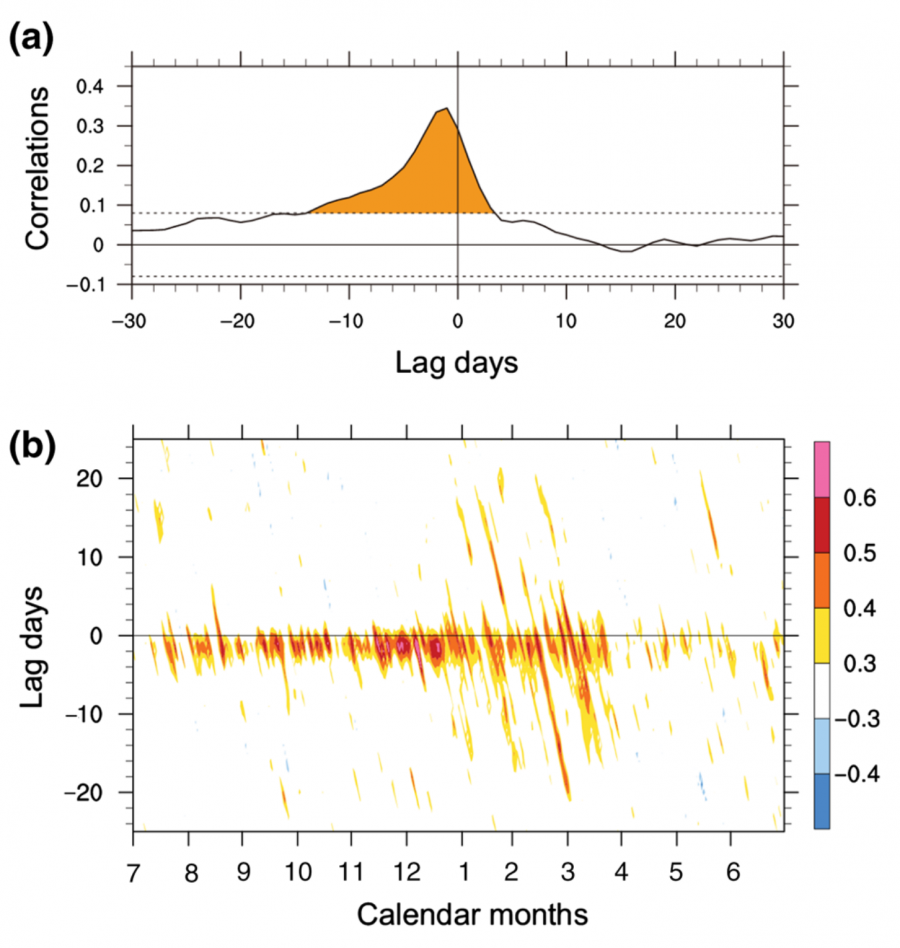
你知道费雷尔环流变化为何超前于北半球环状模变化大约1~2天么?采用表面气压倾向方程可以简单证明,感兴趣的同学可以自行理论推导一下:)。// Do you know why the variability of the Ferrel cell leads that of the the Northern Hemisphere Annular mode (NAM) by about 1–2 days? A theoretical analysis based on the surface pressure tendency equation can demonstrate that. Please have a try by yourself :). For more details please read Li et al. (2014).